takes the series back in time to cover the period following the World Trade Center bombing, mere weeks into Bill Clinton’s first term, and invites players to compare the dynamics of this earlier period. Despite some obvious differences in how the US fought against Islamist terrorism in the 1990s, the Labyrinth series mechanics are a perfect fit for the era given their strategic, geopolitical scope.
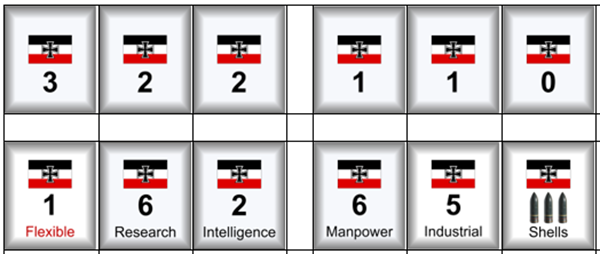
The rules and images shown here are not final.
I’ve always
been interested in games. When I was young my older brother and I used to play
the classic board games like Risk. Even then I would enjoy imagining
designing it into something different, and more realistic (such as I could
understand back then).
We also used
to play games like Magic: The Gathering and the Lord of the Rings CCG.
I only got into strategy and politically themed board games much later.
For most of my life I’ve been a console, and PC gamer. One of my earliest
memories is from when I was 4, and my dad ran straight into the first Goomba on
Mario 3 on the NES, because he thought he’d be able to talk to it! Come
to think of it, I’ve always been interested in diplomacy, too…
The first board
games I bought as an adult were Labyrinth and Twilight Struggle.
That was back when I was a grad student – in 2010, I think. I remember considering
the purchase long and hard before committing to buy them through the bgg market!
I’ve been hooked on the hobby since. I still play TS on the app fairly often
(although my rating isn’t terribly impressive), and I’ve obviously just
launched an expansion for Labyrinth on P500.
Regarding
how I got into design – I’m fascinated by the potential and challenges of
representing history with the medium, and started dabbling in design after
graduating from a PhD in History in 2014. My first idea was to produce a game
on the Cold War (one day…). Design scratches the itch the PhD used to –
research, learning, and creating outputs.
I then got
involved in playtesting for GMT a couple of years before Covid-19, working on The
Weimar Republic (which, crazy to say, will ship soon!). After that, things
accelerated during the pandemic. I got closely involved with Congress of
Vienna, and then The British Way, and made a circle of designer and
developer friends through the COIN Discord server. It’s fantastic being part of
a small group who support one another’s efforts.
The
experience, confidence, and contacts I gained playtesting eventually led to my
being hired for a time as a Staff Developer for GMT, which filled a day per
week when I went down to a 4-day week in my main line of work. Then, after
about 15 months working at GMT I decided I wanted to try my hand at working for
myself, and driving my own projects forward instead of supporting others’ so I
left to pursue freelance opportunities. Game design is a component of that,
alongside a little bit of development here and there. I’m still the Develop for
GMT’s 1848: The Springtime of Revolutions, and Firefight Tactical
because both are such great designs (as someone with a background in the
history of 19th century political philosophy, I really kicked myself
for not thinking to apply 1989’s system to 1848!).
Anyway –
hopefully including a little of my bio will be of interest to anyone
considering going down the path of board game design / development!
-How did the idea of creating this expansion come about?
The project
grew out of the question "Would Labyrinth work well
enough to cover the 1990s, and what would need to change from the base game for
it to do a reasonable job?". I initially approached this as a design
exercise, however, when I gave it a go I was surprised to learn that the answer
was “not a lot”. So, I just kept going with it.
The game
covers the Clinton years, and Bush Jr. up to 9/11, starting in 1993 right after
the WTC Bombing. This frames the expansion between the two WTC attacks and
allows for the major conflicts of the period to have started already. I did consider going from 1988, but that
meant a lot of events needed to go towards setting up the big conflicts of the 1990s,
namely: the civil wars in Algeria and Afghanistan, the wars in Chechnya, and
the UN/NATO interventions in Somalia, Bosnia, and Kosovo.
I have three
central arguments or "theses" that have informed my design decisions:
First, that
the conflict represented in Labyrinth didn't start with 9/11 for the
Jihadists. For them, the fight with America and its allies began with the
Soviet withdrawal from Afghanistan and the collapse of the USSR. After all, Osama
Bin Laden had declared Jihad on the US in 1996, and Al-Qaeda launched a series
of attacks on US targets which started in 1998.[1] The “War on Terror” was a phase in a much longer period of Western engagement
with the Middle East. Within this, 9/11 and the military operations which
followed it were events of huge significance, but nonetheless events that that occurred
within a broader pattern of conflict, and one that predated them. The prequel
therefore allows us to put 9/11 in the broader context of US engagement with
the Muslim world, and even to reframe the "War on Terror" as a
specific phase within that.
Third, before
9/11 the Jihadist movement was split between "nationalist" and
"internationalist" tendencies. Al-Qaeda's
"internationalist" perspective became ascendent in the latter half of
the period, but this was in response to the failure of the
"nationalist" insurgencies in Algeria and Egypt. I have to emphasise
that this isn’t an original argument – inf act it’s just the conventional
historiography – but it is the major design challenge the prequel needed
to meet.
In my view, Labyrinth is
very well suited to telling these stories. Indeed, the base game's Victory
Conditions and mechanics already facilitate this.
-This game starts before the war on terror, how did this affect the two factions?
As
mentioned above, Labyrinth’s systems are well suited to the era given the
geostrategic scope of the game. The Victory Conditions in War on Terror for
example already provide what the prequel needs. There are some oddities porting
a system designed to model the post-2001 period, of course, but Volko always
designed the game in terms of the US and its supporting Coalition battling a
diverse array of Jihadist insurgents. One example oddity is the name of the
“Global War on Terror” track – that needs a little suspension of disbelief!
But there
are differences, of course. For example, in the 1990s the American role was
much more indirect. Dig into the history, though and you’ll find they were always
active in the region – not only supporting existing allies like Egypt against
the insurgency of the Egyptian Islamic Jihad and Al-Jama'a al-Islamiyya, for
example, but also doing things like promoting democracy and good governance in
Algeria in response to the civil war there.[2]
Then, the
US was also very active militarily as part of UN and/or NATO missions in Somalia,
Bosnia, and Kosovo. UN observers were also dispatched to Tajikistan in the
early 1990s, and later, the possibility of the US putting “boots on the ground”
in Afghanistan was even debated by the National Security Council as a possible
response to Bin Laden (it was rejected on the basis the US public wouldn’t
understand or support such a mission).
The
expansion is therefore offered with this framing in mind: that the Labyrinth
series is fundamentally about the engagement of the US led West with the Middle
East, and their conflict with attempts by various Jihadists (mostly Salafists)
to overthrow local regimes.
In terms of
changes to the factions, the main impact is on the Jihadist side. At the start
of the era depicted in the prequel (1993-2001), what we call the “Jihadist”
movement was an international network, but one focused on overthrowing regimes
in Muslim countries that they felt were acting against the interests of Islam
and the Muslim community (Ummah). So, while Salafi insurgents were
spread across the Middle East, and people, ideas, and resources were moving through
international networks
in increasing volumes,
the movement was dominated by a “nationalist” outlook. Jihadists were
strategically focused on fighting the “near enemy”, an approach was
characterized by movements like the Taliban, Egyptian Islamic Jihad, and the
Armed Islamic Group in Algeria.
Proponents
of the approach of attacking the “far enemy” – the United States and the West, meanwhile,
were in the minority. It wasn’t until Al-Qaeda began successfully hitting
American targets that the moral leadership of the movement shifted to Bin Laden
and the “internationalists” – most spectacularly after 9/11, after which groups
began affiliating to the organisation and seeing themselves as local branches
of the larger whole.
This is
represented in Rise of Al-Qaeda in several ways, but the most obvious
mechanical innovation is the introduction of a new unit type, the guerrilla.
These new green cylinder pieces operate as the Jihadist counterpart to the
militia introduced in Awakening. They can be used to count as cells
during Jihad ops and towards Attrition rolls during Civil Wars, but are unable
to Travel or place Plots. They represent locally rooted insurgencies which are
allied to the more mobile terror groups represented by Labyrinth’s cells. The
Jihadist player has less control over the movement as a whole, and also has
fewer cells to play with.
-What new mechanics can we find?
Plenty! Also,
most them can be used as “modules” in the later games as well! (And yes, there
is the option to play through all the games in the series as part of one
campaign).
I’ve
already mentioned guerrillas. Another major innovation is another new unit
type: Russian Troops. This was the era of Russia’s wars in Chechnya, but also
the Tajikistan Civil War, in which Russian forces played a role (hence the UN
observers mentioned above). The expansion needed a way to address this, and
playtesting showed me that it wasn’t going to be appropriate to just do this
through event cards. So, I added a new system, integrated with event cards, to
allow the Russians some limited scope to move and fight.
Alongside
this, there’s a new system of Russian Influence. This helps the Coalition
player by allowing the placement of Russian Troops, but it can also potentially
hamper them – Russian Influence also block War of Idea attempts if Russia’s
posture is Hard, as the Kremlin is in no mood to allow the US-led West to step
in and take over their role.
This means
keeping Russia’s posture Soft can become quite important for the Coalition, and
may also introduce a tension for the Coalition player. I like that this system can
naturally create situations where the Coalition may want the world to generally
adopt a Hard posture, but still feel the need to take Russia to task for using a
military approach. That said, most of the time in Rise the Coalition
will want to adopt a Soft posture. This is the pre-9/11 world, after all, so
the appetite for military intervention is much lower.
You’ll find
Russian Influence counters in all of Russia’s traditional allies across the
region – Serbia, Libya, Syria, and India – and also in their sphere of
influence (the Caucasus and Central Asia). There’s also a solitary Chinese
Influence counter in Pakistan, a longstanding ally of the People’s Republic.
In terms of
the game’s map, there are several changes. There’s a brand new space Bosnia/Kosovo,
and three changes to existing spaces, added to the board as tiles. Caucasus is
now a Muslim Country (representing Chechnya and Azerbaijan), Iraq has become a
special case like Iran (and has a new WMD mechanic), and there’s a brand new
type of space that’s both a Non-Muslim and Muslim at the same time (Israel/Palestine).
Starting
with Israel/Palestine, this is treated as a Muslim Country which also has a
Fixed “Hard” Posture. However, that Posture can be negated if the space becomes
an Ally, and that situation also blocks some nasty Jihadist-aligned events.
This represents Israel changing its policy if peace can be secured with
Palestine. That, may end up a pipe dream, but the game needed to include a
mechanic to made Clinton’s efforts to support the Palestinian peace process
relevant – and this creates the needed incentive.
The
Israel/Palestine space is also a special case in another way, though. It’s now
also always treated as if it has US Troops there. On the plus side for the
Coalition, this means they can always Disrupt there. On the negative, Plots now
harm US Prestige. I introduced this because whilst Palestine is a causes célèbres for Jihadists, there has always been little to
no incentive in the Labyrinth series for the Jihadist player to act
there. This mechanic again redresses this by providing an incentive for
Jihadist Plots.
Iraq,
meanwhile, is no longer a Muslim country the Jihadist might try to take over.
Instead, it’s like Iran. Saddam is still secure in his rule, and three WMD
markers are placed there at the start of the 1993 scenario. A number of event
cards then reference these counters. They give opportunities for players to
gain or lose Funding/ Prestige, and can be removed.
Another
change has also been made to WMDs. As in Awakening, they now reside in
countries that have stockpiles of them: Libya, Syria, one in Pakistan, and yes,
Iraq (note: in the 1990s Iraq did have WMDs – in 2003 they didn’t!). But
anyway, I wanted WMDs to have a more realistic role in the game in two senses.
First, I wanted to change the traditional dynamic of player strategy in Labyrinth
away from Pakistan being a no-brainer Major Jihad. I think history shows us
that the idea of Pakistan falling to insurgents who then use its nuclear
stockpile in terror plots was far-fetched. Second, I wanted them to provide
some protection to the regimes that have them. I’m not 100% sold on this
implementation just yet, but since the main purpose of WMDs is deterrence, for
now they block Regime Change in a space. Since their other main use is for
protection in extreme circumstances, they also add +1 to the number of cells
necessary for a Major Jihad to take place. As they stack with Russian/Chinese
influence, this means pulling off a coup in these spaces in now really hard,
which I think befits the reward for the Jihadist being game-winning WMDs.
However, these spaces are now trickier for the Coalition player to work with.
One impact
of these changes which I wanted to design into the prequel is that the
Jihadists are much less likely to attack regimes which historically aided and
abetted them. But it also means the Jihadist player doesn’t get a free ride in
Muslim Countries at Adversary, in conditions where it’s really difficult for
the Coalition player to respond!
Overall,
these changes – and the design of the card deck – means Rise of Al-Qaeda has
much more of a cat-and-mouse feel to it. I have found through testing that these
changes add more tension and direct conflict to the game, even though the
overall tempo has been reduced (e.g. there are fewer 3-Op cards, making it
harder for the US to change Posture and launch Regime Change, though not
impossible).
That covers
the big changes. There are others in how the card deck works, but this answer
has gotten very long already and I want to save something for InsideGMT!
-Can you recommend some bibliography to help us get into the scene?
I’ve
published a list of recommended sources on the bgg forum for the game (5th
post).
·